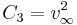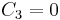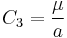Characteristic energy
In astrodynamics a characteristic energy (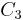 ), a form of specific energy, is a measure of the energy required for an interplanetary mission that requires attaining an excess orbital velocity over an escape velocity required for additional orbital maneuvers. The unit of the characteristic energy is km2s-2.
), a form of specific energy, is a measure of the energy required for an interplanetary mission that requires attaining an excess orbital velocity over an escape velocity required for additional orbital maneuvers. The unit of the characteristic energy is km2s-2.
Characteristic energy can be computed as:
where 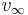 is the orbital velocity when the orbital distance tends to infinity. Note that, since the kinetic energy is one half m
is the orbital velocity when the orbital distance tends to infinity. Note that, since the kinetic energy is one half m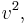 C3 is in fact equal to twice the magnitude of the specific orbital energy (
C3 is in fact equal to twice the magnitude of the specific orbital energy (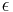 ) of the escaping object.
) of the escaping object.
Contents |
Parabolic trajectory
For a spacecraft that is leaving the central body (e.g. earth) on a parabolic trajectory:
Hyperbolic trajectory
For a spacecraft that is leaving the central body on a hyperbolic trajectory:
where
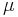 is standard gravitational parameter,
is standard gravitational parameter,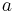 is length of semi-major axis of orbit's hyperbola.
is length of semi-major axis of orbit's hyperbola.
See also
References
- Wie, Bong (1998). "Orbital Dynamics". Space Vehicle Dynamics and Control. AIAA Education Series. Reston, Virginia: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics. ISBN 1563472619.